This form of psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory disease that mainly affects:
- Palms.
- Areas between the fingers.
- Hands.
Very often, people suffering from this form of the disease develop serious psychological complexes.
This form of the disease does not pose a serious threat to human life, however, with the development of severe forms, this disease can be accompanied by the development of a number of very serious complications.
One of the most common complications is damage to the joint area of the lower and upper extremities. This complication leads to the development of psoriatic arthritis. This disease is quite dangerous, as it can lead to the development of temporary disabilities and even disabilities.
Most people with hand psoriasis are diagnosed with lesions that appear specifically on the palms and soles of the feet.
This form of the disease causes the patient many different inconveniences, since the main foci of the development of this disease cannot be hidden under clothes, and the formation of cracks is accompanied by the appearance of painful sensations.
The lesions themselves are small, pink plaques. The plaques stand out strongly above the surface of the skin and eventually become covered with gray scales.
In some cases, the formation of yellow pustules is observed.
The main symptoms of the development of this form of the disease:
- Dry skin.
- Thickening of the skin.
- The appearance of redness.
- Appearance of cracks.
- The appearance of callus-like formations.
Causes
Among the many factors that can cause the disease are:
- Allergic reactions;
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Diseases of the kidneys, liver and pancreas;
- Excess weight;
- Metabolism and dysfunction of the endocrine system;
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Chronic depression, stress or nervous tension.
As we have already noted, the exact causes of psoriasis have not yet been determined. Experts have not been able to establish exactly what causes psoriasis and in which cases it occurs.
At the same time, diseases or moments that cause skin damage in the patient have been identified:
- Inheritance.
- Immune system disorders and metabolic problems.
- Psycho-emotional overload.
- Bad habits and eating disorders.
- General intoxication.
- Viruses, bacteria, fungal infections.
- With a sharp change in climatic living conditions.
- In case of chronic skin diseases.
- If the patient takes drugs from different pharmacological groups for a long time.
Sometimes the manifestation of the disease can occur if a person uses detergents that deprive the skin of its natural coating. It is important to remember that since psoriasis is not contagious, there is no need to worry too much about personal hygiene.
Various factors can cause hand eczema:
- hereditary predisposition;
- weakened immunity;
- disruptions in the functioning of endocrine glands;
- changes in hormone levels;
- chronic diseases;
- infections;
- nervous tension;
- frequent stress;
- constant exposure to chemicals (detergents, paints, solvents) on the skin;
- uncontrolled use of drugs (for example anti-inflammatory drugs);
- clothing made of synthetic fabrics;
- rings and bracelets made from certain alloys;
- cheap low-quality cosmetics;
- pollen;
- Poplar fluff;
- animal hair;
- insect bites;
- mold;
- house dust;
- helminth infestations;
- some food products.
The mechanism of psoriasis has not been fully established, but it turned out that it is caused by a violation of skin cell division, in which diseased cells begin to multiply and grow 5-10 times faster. Soon, immune cells join the process and blood vessels grow.
After the cells die, keratinized areas remain on the smooth surface of the skin - convex psoriatic plaques. In addition to genetic predisposition, features of immunity, skin structure, indirect causes that influence the onset of the development of psoriasis have been identified.
Recent medical research shows a connection between the disease and other pathologies:
- metabolic disorders (diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, increased production of free radicals and nitrogen oxides involved in skin keratinization);
- atherosclerosis;
- cardiovascular disease;
- liver and kidney diseases;
- osteoporosis;
- obesity.
Risk factors include the following:
- to smoke;
- alcohol abuse;
- change in weather conditions.
It is not possible to become infected through contact with a sick person; there are no external carriers of the disease. The inflammatory process occurs in the body and a genetic predisposition to a characteristic disease cannot be ruled out. Other causes of psoriasis on hands are detailed below:
- altered metabolism;
- hormonal imbalance;
- professional risk;
- tendency to allergic reactions;
- presence of bad habits;
- poor nutrition;
- immune disorders of the body;
- violation of personal hygiene rules.
The dermatosis is heterogeneous. There are exogenous and endogenous triggers of the disease.
Exogenous factors include changes in environmental temperature, bad habits, prolonged use of medications, infections, injuries and an atherogenic nutritional profile. Endogenous factors include hereditary predisposition, weakened immunity, stress and sensitization of the body.
Provocative factors trigger the development of the pathological process. Modern dermatologists tend to consider psoriasis of the palms and soles to be the result of a combination of several triggers.
The causes of the disease are not fully understood. Scientists identify several theories:
- Psoriasis is a genetic disease.
- Psoriasis appears due to disorders of the immune, endocrine and nervous systems.
- Psoriasis is a disease that appears due to poor ecology and the accumulation of harmful substances in the body.
When these reasons combine, psoriasis appears. However, the main factor remains genetic: scientists have identified several genes responsible for the onset of the disease.
Factors that provoke the appearance of psoriasis:
- stressful situations;
- hazardous industries, especially those with high concentrations of phenols;
- wounds, abrasions, burns: sometimes psoriasis appears in these places;
- alcohol, smoking;
- infections: especially streptococcal;
- incorrect selection of some drugs.
Why does palm psoriasis develop?
Psoriasis can appear in a person regardless of age and gender. However, there are some statistics that indicate the frequent development of the disease between the ages of 30 and 50.
Scientists have found that the main reason for the development of the disease is the dysfunction of the human immune system and genetic predisposition. However, these facts have not been fully proven and to this day the obvious causes of psoriasis remain unclear. The main factors that provoke palmar psoriasis include the following reasons:
- Decreased immunity.
- Mechanical damage to the palms.
- Frequent hand contact with water.
- Contact of the skin of the hands with chemicals, for example household chemicals, as well as various products at work.
- Often the cause is diseases such as scarlet fever, chronic tonsillitis, kidney disease and other diseases.
- Oncology.
Doctors attribute alcohol abuse, drug use and some medications as another cause of the disease.
The main manifestations of palm psoriasis
It is worth noting that this type of disease occurs mainly in people who perform physical work associated with stress on the hands. In medical practice it is customary to distinguish three types of diseases. These include:
- Fan-shaped plaque.
- Circular.
- Calloused.
Types of psoriasis on the hands
| Localization of psoriasis on the hands | Description of the problem |
| On the palms | Redness of the surface of the skin of the palms, itching, roughening of the upper layer, the appearance of calluses. Outwardly, many people confuse palmar psoriasis with mycosis or eczema. To make a correct diagnosis, you need to consult a specialist. |
| On the hands and fingers | Inflammation, swelling of the fingers, scaling, cracking of the skin, pain and itching. |
Depending on the localization of the process and the specific location where the primary lesions appear, different types of hand psoriasis are distinguished:
- Pustular: the most dangerous type, affects any skin. First, small spots appear on the phalanges of the fingers and palms, involving the nails. Then the spots coalesce, fill with pus, the lesion spreads to the hands and other areas, causing swelling and degenerative changes in the organs.
- Drop-shaped: The rashes are pale pink, convex, shaped like small drops. It is localized on the shoulders and forearms and grows to cover a large area.
- Nails – This type of psoriasis leads to changes in the appearance of the nails and nail beds. A "thimble symptom" is observed when the color of the nail plates changes and small indentations and grooves form on them. At the same time, the nails thicken and begin to peel off, until they are completely lost.
- Plaque (vulgar) – ranks first in prevalence. These are typical psoriatic plaques with a tendency to merge and form "paraffin lakes". They appear above the elbow joints, on the extensor surface of the arms and affect the palms of the hands. Palmar psoriasis is characterized by swelling of the epidermis and the formation of callus-like tubercles on the surface of the dermis.
Stages of the disease
In the initial phase of hand psoriasis, even before the first rash appears, the following disorders can be recognized:
- swelling is observed in the joint area;
- the skin takes on a reddish tint in some places;
- the nails become inflamed.
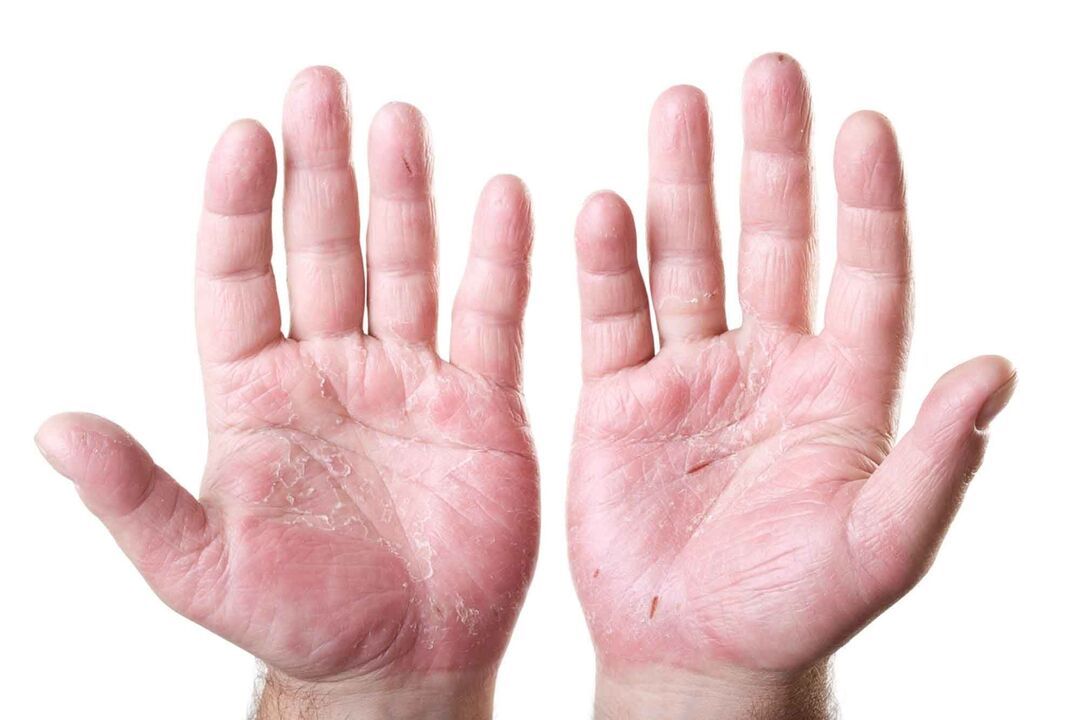

The following stages of psoriasis on the hands are distinguished:
- Exacerbation is a progressive stage of the disease. It is characterized by an increase in the number and size of the spots, increased itching and scaling.
- Stationary stage - is characterized by attenuation of the disease, change in the color of the psoriatic plaques (they become less red, more white) and a decrease in the spots.
- The remission phase is characterized by the complete disappearance of all signs of psoriasis.
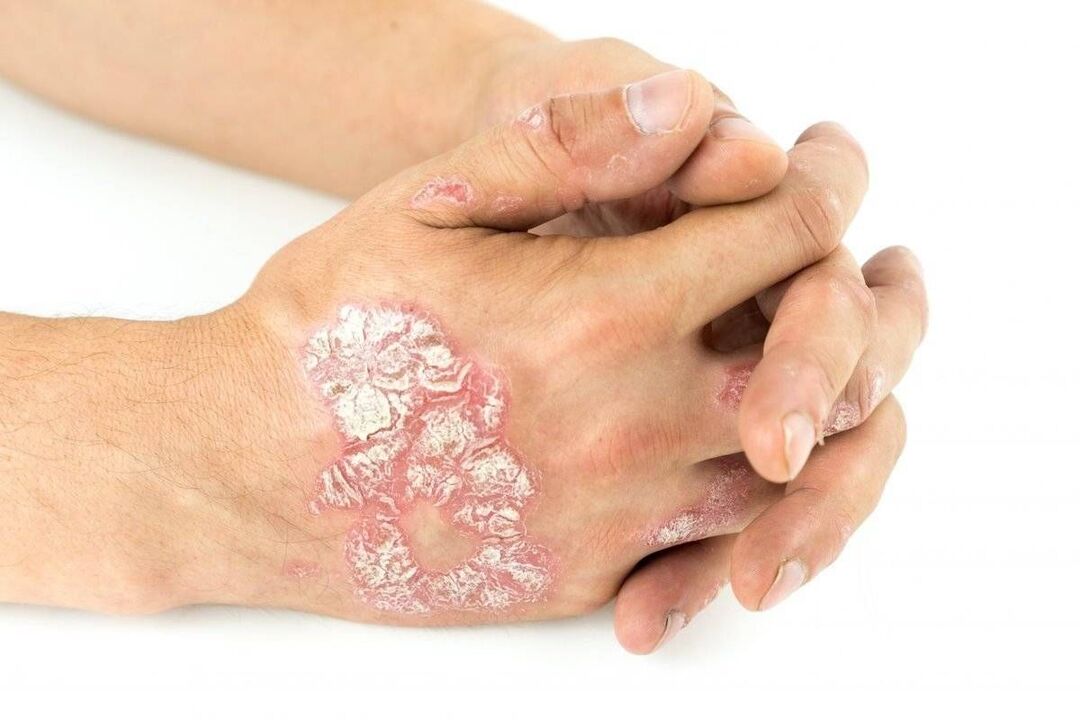
Looking at hands affected by psoriasis is extremely unpleasant. But the disease is so common that people need to know what psoriasis looks like on their hands in order to detect the problem in time and start treatment of the disease in a timely manner.
Hand psoriasis develops gradually. Doctors note that in medicine there are several stages of the disease, which imperceptibly replace each other in the absence of timely therapy. The clinical outcome for the patient depends entirely on timely response therapeutic measures. The development and signs of the different stages of upper extremity psoriasis are as follows:
- Initial state. The small round papules have clear boundaries. Initially they are solitary, but after 2-3 days from the desquamation of the dermis they expand covering large areas of the lesion.
- Progressive phase. Painful nodules are distinguished by a bright red tint, and peeling of the epidermis with crusting is observed in the center. The pathology is preceded by microtraumas of the skin.
- Stationary stage. The rashes, once red, turn bluish and dry out. The inflammatory process decreases in intensity, itching stops, but hyperemia of the skin is present.
- Regressive phase. Local manifestations of psoriasis reduce the intensity and once the painful lesions resolve. There is a long period of remission, no peeling, but white spots with clear borders are visible.
Psoriasis of any form and location, including psoriasis of the skin of the hands, goes through 3 stages:
- Progressive stage (exacerbation): the spots grow, new ones appear, the manifestations of psoriasis intensify.
- Stationary stage: the manifestations of the disease fade, the spots become pale and decrease in size.
- Regressive stage (remission): the manifestations disappear completely.
The initial stage of psoriasis of the arms and hands can manifest itself in different ways: weak, barely noticeable, or immediately bright spots appear, as in the acute phase (less often).
Features of therapy in pregnant women and children
Due to the weakened immunity of the mother and the immature immune system of the child, treatment of eczema on the fingers requires:
- Adjustment of the diet of a breastfeeding mother and child, limiting milk intake, eating green fruits and vegetables and fermented milk products. At an older age, it is necessary to exclude flour products, smoked meat and foods rich in salt from the child's menu.
- Taking vitamin complexes to support the immune system of a pregnant woman.
- One of the recommended measures is to limit contact with household chemicals and water.
- Use of antihistamine ointments or dermatotropic agents.
For the treatment of children the following drugs can be prescribed:
- Production of boric acid-based lotions
- Taking calcium-based drugs, taking into account the reduced content of this microelement, characteristic of this pathology in children.
- The use of ointments containing antibiotics is practiced to relieve the symptoms of serious infections.
- The use of antihistamines to reduce the intensity of itching.
A set of measures aimed at the recovery of the mother and child should include compliance with personal hygiene rules and maintenance of hygienic conditions of the premises.
Psoriasis on the hands
Official medicine classifies hand psoriasis as a chronic disease with a multifactorial etiology. This means that the exact causes of the disease have not been established and doctors consider them as possible factors. Doctors classify it as a skin disease based on its main symptoms: red scaly plaques that appear on the skin. But the culprit of the disease is hidden deep within the human body.
In the course of long studies of the mechanism of development of psoriasis, scientists have identified a connection with autoimmune failure.
The first signs of psoriasis appear on the hands in the form of small red papules with clear outlines. 2-3 days pass and the papules become covered with scales. A long process of disease progression then begins, characterized by periods of exacerbation and remission. Therefore, psoriasis that initially occurs between the fingers can spread to the entire surface of the palm. Individual plates grow and fuse, forming a continuous scaly crust. The photo clearly shows what psoriasis looks like on your hands.
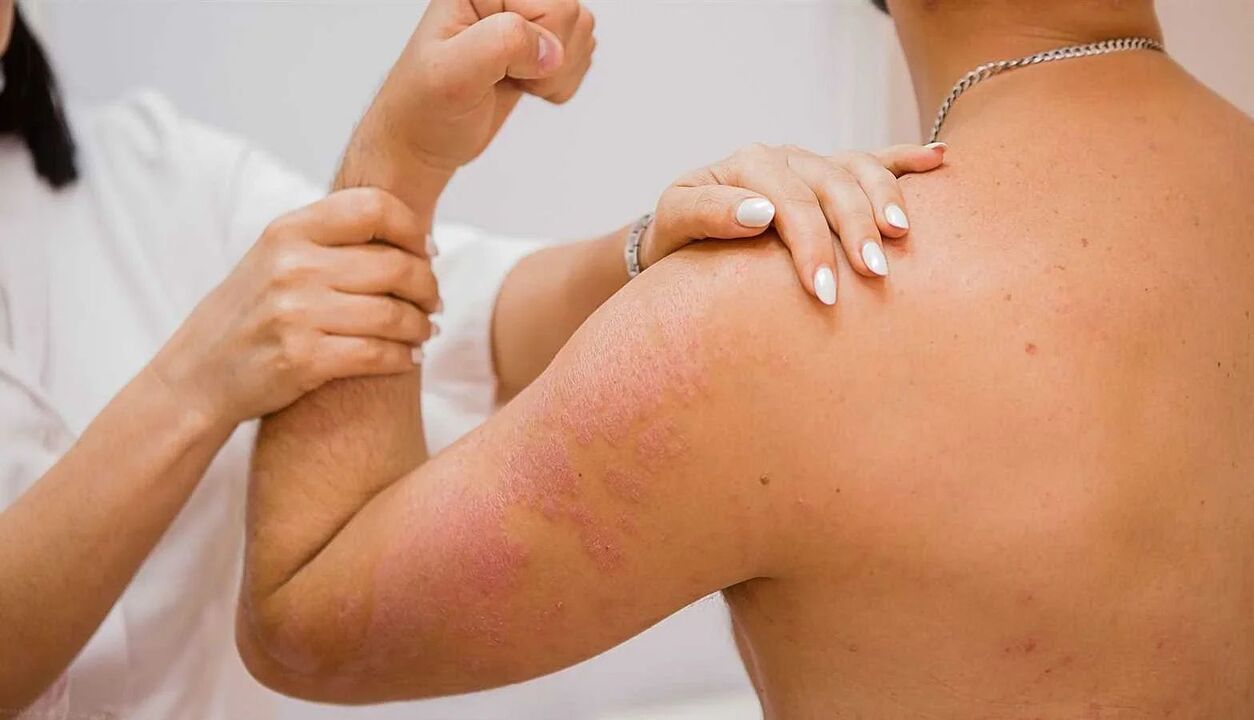
The first changes shape on the back of the hand, gradually affecting the sides of the hand. Imperceptible at the beginning of the negative process, they lead to an obvious cosmetic defect, when it is already difficult for a person to hide the presence of the disease. What could happen?
Symptoms of psoriasis on the hands
The characteristic symptoms of psoriasis on the hands should be considered in the context of their manifestation on any part of the patient's body. When the lesion begins, small areas of the dermis are affected, but the process does not end there and over time the plaques can cover the entire hand. The general symptoms look like this:
- the appearance of small papules;
- formation of encrustations;
- dryness and flaking of the skin of the hands;
- nails lose their natural color, their structure changes;
- signs of skin hyperemia;
- the skin in the affected area becomes reddish;
- pain appears in the joints;
- feelings of internal discomfort.
We have given the general signs of the disease, but experts divide them according to the stages of the disease.
What forms of disease exist?
The versatility of the manifestations of psoriasis encountered by doctors forced them to describe the various forms of the disease. Experts have combined the existing species into two main groups: pustular and non-pustular.
The pustular group includes the following forms of the disease:
- generalized;
- similar to annular centrifugal erythema;
- palmoplantar.
The non-pustular group contains:
- classic form of psoriasis with early or late onset;
- psoriatic erythroderma.
The presented classification does not include such types of diseases as seborrheic, exudative psoriasis, napkin disease, atypical and drug-induced psoriasis.
Reasons for the formation of psoriasis on the hands
Of all places affected by the disease, hands account for 85% of all diagnoses. Many years of observation of patients suffering from an unpleasant disease have led scientists to the conclusion that the causes of psoriasis on the hands depend on the gender and age of the patient.
Psoriasis is extremely rare in black people. A scientific explanation for this fact has not yet been received.
What causes psoriasis on women's hands?
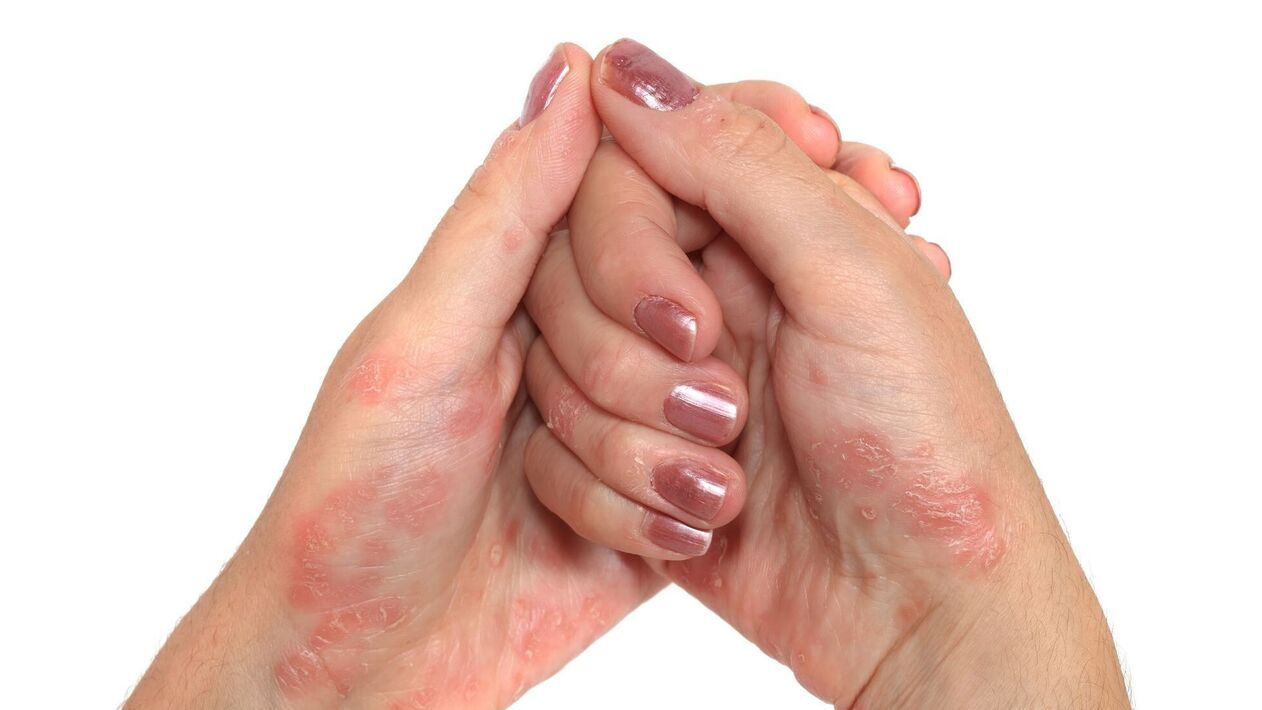

What doctors call genetic predisposition is the main reason. Interestingly, even though the woman's parents did not have psoriasis, one of her relatives probably had such a diagnosis. Other reasons include:
- climatic characteristics (very humid, cold or hot);
- hormonal imbalances;
- bad habits (alcohol, smoking, drugs);
- stress and nervous tension;
- taking antibiotics, some vaccines, overdose of vitamin preparations;
- wounds, burns, cuts.
These same reasons can cause an exacerbation of the disease. It is difficult to eliminate the listed factors from your life, but some of them can be eliminated.
What causes psoriasis on men's hands?
Trying to identify the main ones, doctors were forced to admit that they could not establish them with high accuracy. The basis for the onset of psoriasis in the hands of men is a malfunction of the immune system, which is expressed by:
- improper metabolism;
- imbalance of lipid and carbohydrate metabolism;
- increased sugar levels;
- cholesterol.
A greater chance of developing psoriasis awaits men who already have people in their family who have suffered from this disease. The reasons may be:
- chronic lack of sleep;
- poor nutrition;
- cold climate.
Those who moved from the southern country to the northern region say that the cold climate causes an exacerbation of the disease and is difficult to treat.
Causes of psoriasis on children's hands
In recent years, cases of diagnosis have become more frequent. It often takes a generalized form, with plaques covering large areas of the body. The first thing that is determined as the cause of the disease is a hereditary factor. According to statistics, among parents of patients suffering from psoriasis, the child will inherit the disease in 50% of cases. In addition to genetics, the disease can be caused by:
- childhood infectious diseases (measles, ARVI, tonsillitis);
- stressful situations;
- severe fear, loss of a loved one;
- heat stroke;
- unbalanced diet;
- hypothermia of the body;
- predisposition to allergies.
Diagnosis of the disease
It is enough for the doctor to know what psoriasis looks like on the hands to make an accurate diagnosis. No specific studies are carried out to establish the disease. If the patient states that the plaques on his hands have appeared for a long time, the doctor may prescribe additional tests. Their list includes:
- blood biochemistry;
- general blood test to determine the amount of ESR;
- tests for rheumatoid factor and the presence of specific proteins;
- a biopsy performed to detect immature skin cells, accumulations of rete bodies, macrophages, and T leukocytes.
How to treat psoriasis on hands?
Treatment of psoriasis on the hands depends entirely on the stage of the disease. Although the disease cannot be cured, when using an integrated approach to treatment, the symptoms become almost invisible, and remission lasts a long time.
External means
In the initial and intermediate stages of the disease it is sufficient to use drugs for external use. These can be creams and ointments of different groups:
- Not hormonal. As a rule, they do not give side effects and their effect is mild and delicate.
- Hormonal.
These remedies are used when pronounced symptoms appear (persistent rash, brittle nails) when other ointments do not help. Prescribed only by a doctor, they can have strong side effects. The frequency and duration of use of external agents depends on the severity of the symptoms: 1-2 times a day for 10-20 days. A break is necessary after each course.
Systemic drugs
Tablets and injections are prescribed when external drugs are ineffective in advanced stages of psoriasis on the hands:
- Tablets: antihistamine, anti-inflammatory. Drugs from the cytostatic groups, monoclonal antibodies, immunosuppressants, immunomodulators, sedatives and vitamins are also used.
- Injections: antihistamines, hepatoprotectors, immunosuppressants, immunomodulators, hormonals.
The form and type of the drug depends on the stage of the disease and the intensity of its manifestations. The use of systemic drugs is carried out only under the supervision of a doctor.
Physiotherapy and traditional methods
Psoriasis is a long-term disease with multiple symptoms. Therefore, the treatment is always complete. Alternative methods can be used:
- Physiotherapy: phototherapy, bioresonance and PUVA therapy, cryotherapy, ozone therapy, ichthyotherapy.
- Folk remedies: birch tar, linseed or sea buckthorn oil, aloe, bay leaf, baking soda, sea salt, etc.
Their purpose and use should also be agreed with a dermatologist.
Use of herbs
Many medicinal herbs have the following properties:
- anti-inflammatory;
- regenerating;
- antibacterial.
To treat palm psoriasis, celandine, St. John's wort, horsetail, oregano, nettle and others are used. An infusion or decoction is prepared from herbs. They are also used to add to the bathroom.
Soda treatment
One of the methods offered by alternative medicine to get rid of psoriasis on the palms is treatment with ordinary baking soda. Its use has the following effect on the affected skin:
- cleaning;
- sweetening;
- elimination of inflammatory processes;
- improvement of local blood circulation;
- eliminates peeling;
- relieves itching.
The recipe for preparing a solution for external use is quite simple: dilute a certain amount of product in purified water. You should obtain a viscous and pasty mixture. This product should be applied to the areas affected by the disease. There is no need to rinse.
Prevention: what rules to follow
It will be easier to treat hand psoriasis if, if possible, the factors that cause it are eliminated or minimized. In this case, the treatment will be much more effective and the progression of the disease will stop.
Correct therapy, even at the initial stage, can only be prescribed by a specialist, so the examination is mandatory. As well as using all available methods and means: from ointments and creams to injections, compresses and physiotherapy. The doctor will prescribe the order and dosage, but one should not forget about prevention even in the regression phase. Hands should be treated with the utmost care: use of protective creams and exclusion of aggressive household chemicals.
























